An increasing awareness of environmental impacts and collective calls for better sustainability are leading to a time of transformation in the mining industry, where companies are navigating the shift to greener operations.
Due to the impact that mining exercises can have on the natural environment in mineral-rich areas, as well as the by-products of industrial mining operations such as pollution, mining companies are under pressure to better consider how they can practice better environmental stewardship.
This article discusses the top 10 sustainability challenges facing mining operations today and how these can be approached. The journey towards sustainability is complex, but necessary for the mining industry to ensure its relevance and resilience in the face of an evolving global ethos.
1. Carbon Footprint
The mining industry encompasses a large variety of activities, from extraction to transportation and processing; almost all of these involve the generation of direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions. The University of Queensland estimates that greenhouse gas emissions associated with primary mineral and metal production was equivalent to approximately 10% of the total global energy-related greenhouse gas emissions in 2018.
To minimise their environmental impact, mining operations must focus on energy-efficient practices and renewable energy adoption. Strategies could include:
- Implementing advanced technologies
- Transitioning to renewable sources like solar and wind power can significantly reduce carbon emissions.
- Electric mining vehicles and alternative fuel sources such as green hydrogen also offer room for improving carbon footprint.
2. Water Conservation
Water is a crucial resource in mining activities, used extensively for mineral processing, dust suppression, and in extraction processes. However, the excessive water consumption of mining operations poses a threat to local water sources and exacerbates global water scarcity concerns.
To address this challenge, mining companies must adopt efficient water management strategies. Implementing closed-loop systems, recycling water, and employing advanced technologies can significantly reduce water consumption in mining processes. Sustainable water practices are not only vital for preserving local ecosystems but are also integral to the industry’s long-term viability.
3. Site Rehabilitation
Site rehabilitation is a critical aspect of responsible mining, ensuring that ecosystems disturbed during mining activities are restored. This involves addressing soil erosion, replanting native vegetation, and reclaiming disturbed land. Mining’s impact on the environment extends beyond extraction, making effective site rehabilitation a key sustainability challenge.
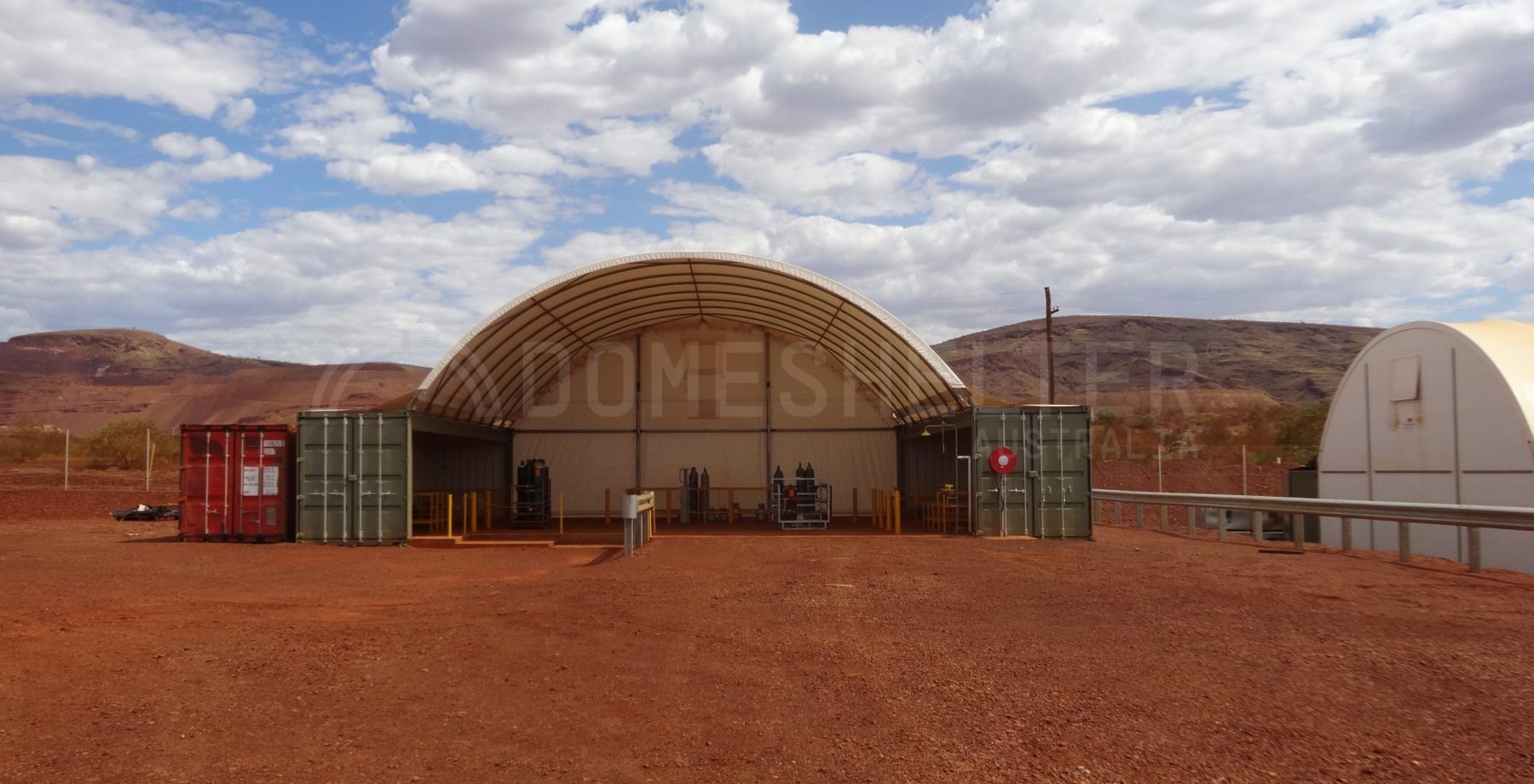
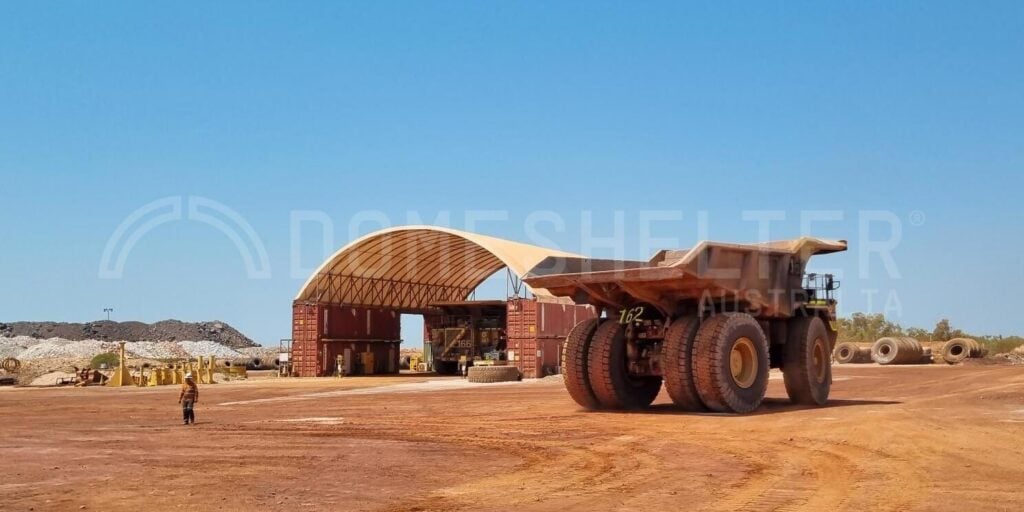
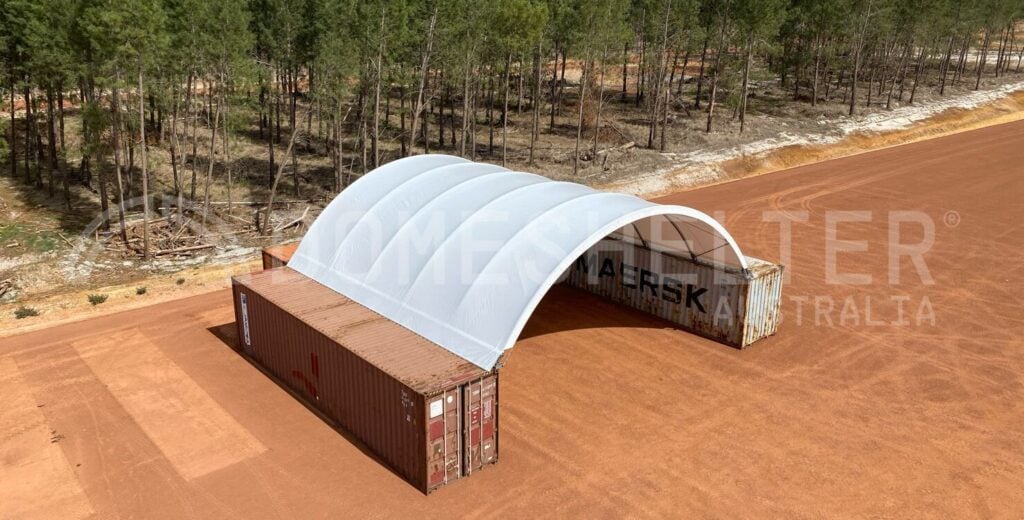
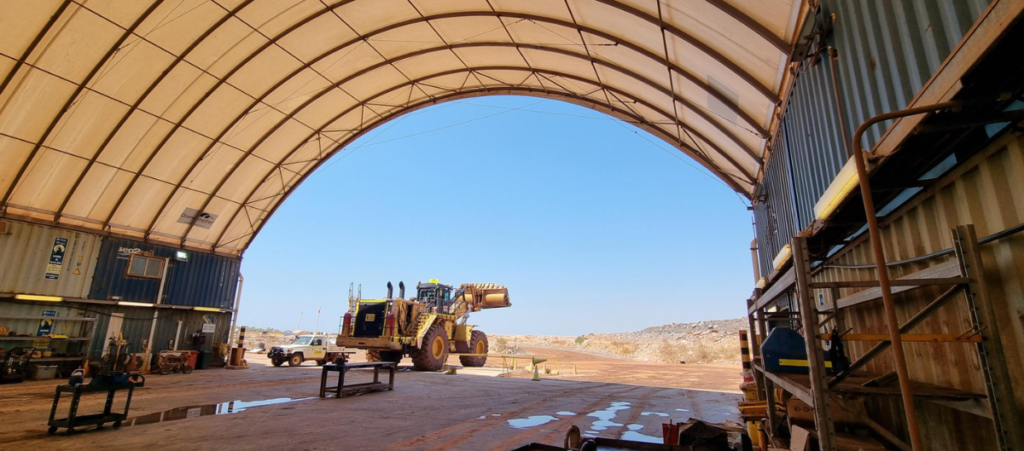
Infrastructure choices play a pivotal role in site rehabilitation efforts. Opting for structures that require minimal ground disturbance, such as DomeShelter™ Structures, can significantly ease the rehabilitation process. These fabric-covered shelters provide a durable and flexible solution without the need for extensive foundations, allowing for quicker and more efficient restoration of mined areas. As the mining industry pivots towards more sustainable practices, the role of low-impact infrastructure becomes increasingly vital in ensuring successful site rehabilitation.
4. Community Relations
Effective community engagement is crucial for mining companies aiming to properly balance the economic benefits of operation while minimising negative impacts on local communities. The social license to operate in any given region depends on fostering positive relationships, addressing concerns, and actively involving local communities in decision-making processes.
To build and maintain positive community relations, mining companies can implement sustainable practices that prioritize the well-being of local residents. This includes:
- investing in community development projects
- Providing job opportunities
- Respecting local cultures and traditions
Transparent communication and collaboration with local stakeholders are essential elements in establishing trust. By adopting practices that go beyond regulatory requirements, mining operations can contribute to the socio-economic development of the communities they operate in, creating a win-win scenario for both the industry and local residents.
5. Biodiversity Preservation
Mining activities often intersect with diverse ecosystems, raising concerns about their impact on biodiversity. It’s crucial for companies to assess these impacts and explore measures that allow mining to coexist harmoniously with natural habitats.
Mining operations can significantly affect biodiversity by disrupting ecosystems, fragmenting habitats, and introducing pollutants. To address this, comprehensive impact assessments must be conducted to understand the specific risks and potential consequences. Implementing effective mitigation measures, such as:
- Habitat restoration;
- Conservation initiatives, and;
- The establishment of protected zones
Can help minimise the footprint of mining activities. Finding a balance between resource extraction and biodiversity preservation is challenging but essential for fostering long-term environmental sustainability.
6. Materials Efficiency
Optimising the use of resources and materials is a key consideration for companies looking to improve their sustainability practices. Mining operations are inherently resource-intensive, with the potential to result in significant environmental impacts. For example, various chemicals such as cyanide and sulfuric acid are used in ore processing to extract valuable minerals, and most mine vehicles are run using copious amounts of petrol or diesel.
To address this, companies can adopt advanced technologies and processes that minimise waste generation and maximise resource utilisation. Implementing recycling initiatives, adopting circular economy principles, and exploring alternative materials can contribute to a more sustainable and efficient use of resources in mining.
7. Supply Chain Sustainability
The mining supply chain, which includes extraction, processing, transportation, and delivery, plays a pivotal role in determining the industry’s overall environmental impact. The numerous stages involved have various environmental impacts. It’s crucial to address sustainability concerns across the supply chain to minimise adverse effects on ecosystems and communities.
To enhance supply chain sustainability, mining companies can prioritise responsible sourcing of raw materials, opting for suppliers committed to environmentally friendly practices. Implementing efficient transportation methods, such as using electric or hybrid vehicles and improved logistics practices, reduces the carbon footprint associated with delivery. By adopting a holistic approach to supply chain sustainability, mining operations can begin to minimise their ecological footprint and contribute to a more responsible and environmentally conscious industry.
8. Regulatory Compliance
Navigating environmental standards is a critical aspect of sustainable mining practices. The industry is subject to many regulations, in areas such as emissions, water usage, and land rehabilitation. For instance, compliance might involve adherence to emission limits for mining equipment or the implementation of advanced water recycling systems to meet and exceed water usage standards. Non-compliance may result in legal actions, fines, and penalties imposed by regulatory bodies. Beyond the financial implications, companies may face reputational damage, public scrutiny, and strained relationships with local communities.
Mining companies have an increasing need to adopt proactive strategies to ensure they are operating in compliance with regulations. This can happen in a number of ways:
- Engaging in collaborative partnerships with local communities and environmental organisations can foster a more inclusive decision-making process.
- Implementing advanced monitoring technologies and real-time reporting systems ensures continuous compliance and provides transparent data.
- Investing in research and development for innovative, eco-friendly mining practices showcases a commitment to sustainability and can position companies as industry leaders in environmental stewardship – such as Fortescue.
- Furthermore, actively participating in regulatory discussions and advocating for policies that balance environmental protection with economic interests can contribute to the development of more robust and fair regulatory frameworks.
Get In Touch
DomeShelter Australia has decades of experience in the mining industry, providing leading companies with infrastructure solutions that protect their people and assets from the harmful effects of the elements while also reducing their environmental impact with sustainable Shelter Solutions.
To learn more about how a Fabric Shelter could help meet the sustainability needs of your project, get in touch with the team today, or visit our learning centre to read more.